Understanding the Absolute Net Lease in Commercial Real Estate

What is an Absolute Net Lease
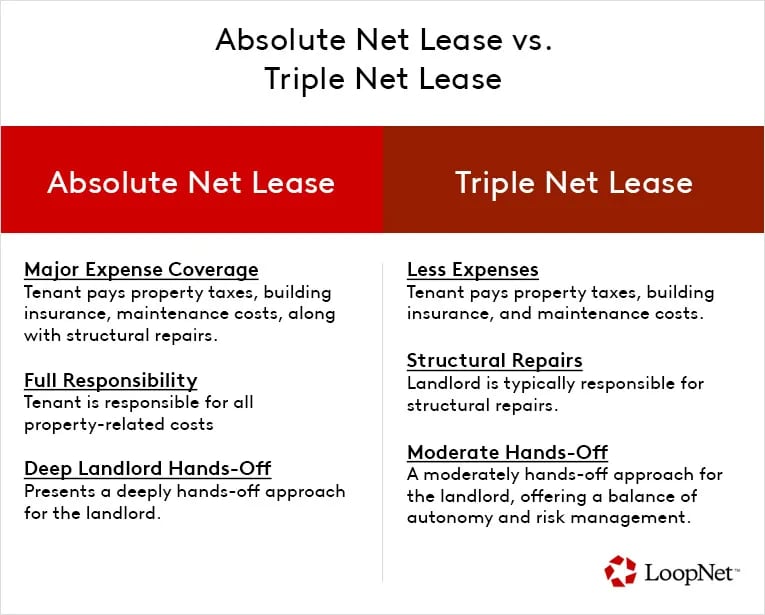
An absolute net lease is a type of commercial real estate lease where the tenant takes on significant financial responsibility. This includes paying for property taxes, insurance, routine maintenance, and even major structural repairs.
Ideally suited for long-term commercial arrangements, the absolute net lease offers a deeply hands-off approach for the landlord, making it a particular form of interest to commercial real estate investing.
Understanding the various lease structures, including an absolute net lease, is foundational. In this guide, we'll dissect the concept of an absolute net lease, compare it to other lease types, and discuss its advantages and potential challenges. By comprehending these aspects, you can make informed decisions that align with your commercial property investment strategy.
Absolute Net Lease vs. Triple Net Lease
Both absolute net leases and triple net leases are common in the world of commercial real estate, but they offer different responsibilities for tenants. Understanding the key differences can help tenants or investors make informed decisions that suit their financial and business needs.
Key Differences Between the Two Lease Types
A triple net lease (NNN) is a lease agreement where the tenant agrees to pay all the operating expenses of the property. These expenses include property taxes, building insurance, and maintenance costs. While this may seem comprehensive, certain responsibility limitations do exist. In a triple net lease, landlords typically handle structural repairs, such as roof or foundation issues.
In contrast, an absolute net lease, takes the tenant's responsibilities further. Like a triple net lease, the tenant agrees to pay property taxes, building insurance, and maintenance costs. However, they also take on the responsibility for structural repairs. This means that if a roof leaks or a wall develops foundational issues, the tenant is responsible for fixing it.
Factors to Consider While Choosing Between an Absolute Net Lease and a Triple Net Lease
When choosing between absolute net and triple net leases, tenants and investors should weigh the advantages and drawbacks of each.
With an absolute net lease, tenants usually have more control over their business premises, including maintenance and repair decisions. This autonomy is somewhat similar to a master lease, where tenants also gain operational control, but master leases allow subleasing rights, making them a flexible strategy for investors seeking additional income opportunities.
However, the high level of responsibility in an absolute net lease might not be suitable for all businesses, particularly if they lack the time or resources to manage property maintenance and repairs. In addition, the unpredictable costs associated with major structural repairs can add a layer of financial risk.
In contrast, a triple net lease offers a less risky alternative as the landlord retains responsibility for the property's structural integrity. For some businesses, this might offer a comfortable balance between autonomy and risk management.
Ultimately, the decision between an absolute net lease or a triple net lease largely depends on specific business considerations, including financial health, strategic business plans, and the available resources for managing property-related matters.
Absolute Net Lease vs. Bond Leases
While absolute net leases and bond leases are both types of commercial real estate agreements, they each have specific features and constraints that can greatly influence a tenant's or investor's decision-making process.
Explanation of Bond Leases
A bond lease, also referred to as a "hell or high-water lease," is a long-term lease agreement and is often regarded as one of the most stringent forms of a commercial real estate lease.
Like absolute net leases, bond leases make tenants responsible for all property-related costs. However, a bond lease takes this responsibility even further.
In a bond lease agreement, the tenant is also obligated to reconstruct the property in the event of its destruction by any unforeseen or catastrophic events, such as natural disasters. As such, the tenant assumes a considerable amount of risk. Additionally, even if the property becomes unsuitable or condemned for occupancy, the tenant is usually bound to continue paying the rent for the lease's duration.
Comparisons with Absolute Net Leases
While both absolute net leases and bond leases place substantial responsibility on the tenant, bond leases extend tenant obligations significantly more. It's crucial for the potential tenant or investor to be aware of these differences when deciding on a lease agreement.
The cornerstone difference is that under a bond lease, the tenant is responsible for rebuilding the property in the event of its total or substantial destruction. This requirement is usually not a part of an absolute net lease.
Moreover, in a bond lease, the tenant is typically obliged to continue rent payments throughout the term, regardless of certain circumstances that could make the property uninhabitable. This commitment isn't common in absolute net leases.
Benefits of an Absolute Net Lease
Absolute net leases provide distinct advantages for both the tenants and the landlords that, when understood and navigated correctly, serve the interests of both parties.
Absolute Net Lease Advantages for Tenants
- Lower Rent: Tenants often receive lower base rents in exchange for assuming most operating expenses. This can result in significant cost savings over the lease term.
- Control Over Maintenance and Repairs: Tenants have the freedom to manage and control property repairs and maintenance, providing a level of autonomy over the quality and timeliness of these services.
- Tax Deductions: Tenants can potentially deduct certain property expenses, such as property taxes, maintenance costs, and insurance premiums, as business expenses on their tax returns, providing possible tax advantages.
- Long-Term Lease Security: Due to the nature of absolute net leases, they often come with longer lease terms. This stability can offer peace of mind to tenants, particularly those looking to establish a long-term presence in a community or business area.
Absolute Net Lease Advantages for Landlords
- Reliable Income Stream: Tenants are typically committed to a longer lease term without the concession of rent reductions or holidays, which landlords can bank on for a stable and predictable income.
- Reduced Operating Expenses: Since the responsibility of property expenses, maintenance, and repair costs rests on the tenant in an absolute net lease, the landlord's operating expenditure is drastically reduced.
- Minimal Property Management: Landlords significantly reduce the management time and effort required for the property, leaving more time for other business development activities or investments.
- Less Risk of Extra Costs: As tenants are responsible for both minor and major repairs, landlords are shielded from unexpected and potentially substantial expenditure related to the property.
Challenges of an Absolute Net Lease
While an absolute net lease carries numerous advantages, both tenants and landlords must also consider the potential challenges intertwined with this lease structure.
Absolute Net Lease Challenges for Tenants
- Unpredictable Expenses: In an absolute net lease, tenants shoulder the responsibility for all property-related expenses. This includes costs that fluctuate or can suddenly spike, such as repair costs for major structural elements, insurance premiums, or any increase in property taxes. This variability can introduce a degree of uncertainty into financial planning.
- Increased Responsibilities: Tenants must manage all property tasks, from minor maintenance to major structural repairs, traditionally handled by the landlord.
- Financial Risks: Tenants are fully liable for any unexpected incidents resulting in substantial costs, whether that be a natural disaster or a sudden need for significant structural repairs. This aspect of risk can be challenging, especially for small businesses or those with tight cash flow.
Absolute Net Lease Challenges for Landlords
- Dependence on Tenant: In an absolute net lease, much hinges on the tenant's ability to effectively manage the property and meet their financial obligations. If a tenant fails to take care of the property or falls behind in payments, the landlord may ultimately have to intervene or bear the financial fallout.
- Potentially Lower Rent: As tenants in an absolute net lease take on more expenses, they may negotiate a lower base rental rate. While this allows a landlord to avoid maintenance costs and other expenses, it could also mean lower revenue compared to traditional gross leases.
- Tenant Turnover and Retention: An absolute net lease may complicate the efforts to attract and retain tenants, especially businesses not prepared to take on the full range of property responsibilities. This dynamic could lead to potential vacancies, which are especially impactful given the long-term nature of absolute net leases.
Both parties entering into an absolute net lease should fully appreciate their responsibilities and consider the possible risks. A careful analysis of the lease terms, cost factors, and one's financial ability to meet the lease's obligations is crucial to making the right decision.
Tips for Investors
Commercial real estate investments can be complex, particularly when considering distinct lease structures such as the absolute net lease. Alongside this, it is crucial to have a clear understanding of the return on investment, measured through indices like the capitalization rate.
Analyzing Tenant's Financial Strength
An absolute net lease depends on the tenant's ability to cover costs and maintain the property. Assessing a potential tenant's financial stability and the tenant's track record in similar leases, or commercial real estate loans, can mitigate the risk of unforeseen costs down the line.
Understanding Lease Terms
When looking at absolute net leases, it's vital to have a comprehensive understanding of lease terms. These terms can vary greatly and not all leases advertised as 'absolute net' uniformly follow the same structure. Additionally, ensuring that you've obtained an accurate commercial real estate appraisal can affect your investment decisions and financial obligations. As an investor, always read through every lease agreement attentively, seek clarifications on uncertainties, and ensure a comprehensive understanding of your responsibilities.
Rely on Professional Guidance
Seeking advice from an attorney or a real estate professional with expertise in commercial leases can assist investors in properly assessing the cost and benefits of an absolute net lease.
In conclusion, an absolute net lease presents a unique proposition in the realm of commercial real estate, offering a balance of benefits and challenges to both tenants and landlords. While it optimizes cost-efficiency and operational responsibilities for landlords, it requires tenants to shoulder broad property-related costs and liabilities. Weighing these considerations is crucial to ensure that an Absolute Net Lease aligns with your investment goals, risk tolerance, and management capacity.
Commercial Real Estate For Lease
