What is a Land Trust? A Secure and Private Way to Own and Manage Real Estate

What is a Land Trust?
A land trust is a legal entity that holds title to real estate, providing a way to manage and protect property ownership. It's a type of trust that allows individuals or entities to transfer ownership of property to a trustee, while maintaining control over the property's use and management.
The purpose of a land trust is to provide a secure and private way to own and manage real estate, while also offering benefits such as reduced liability and tax advantages. By understanding how land trusts work, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions about their property ownership and management strategies.
Types of Land Trusts
Title Holding Land Trusts
Title-holding land trusts are a type of land trust that allows individuals to hold title to real estate anonymously. This type of trust is commonly used for estate planning and asset protection purposes. In a title-holding land trust, the trustee holds the title to the property, while the grantor (the person creating the trust) maintains control over the property's use and management.
Conservation Land Trusts
Conservation land trusts are a type of land trust that focuses on preserving natural resources, such as wildlife habitats, forests, and wetlands. These trusts are often used to protect sensitive ecosystems and promote conservation efforts. Conservation land trusts can be established by individuals, organizations, or government agencies, and can be used to protect private or public lands.
Community Land Trusts
Community land trusts are a type of land trust that focuses on community development and affordable housing. These trusts are often used to preserve affordable housing options for low-income families and individuals. Community land trusts can be established by non-profit organizations, community groups, or government agencies, and can be used to acquire and manage properties for affordable housing purposes.
| Trust Type | Purpose | Used By | Common Assets Held |
|---|---|---|---|
| Title-Holding | Asset protection, estate planning, privacy | Individuals, investors, families | Residential or commercial property |
| Conservation | Preserve natural resources and open land | Nonprofits, government agencies, landowners | Wetlands, forests, habitats, farmland |
| Community | Support affordable housing and community development | Nonprofits, local governments, community orgs | Single-family homes, multifamily units, vacant lots |
How a Land Trust Works
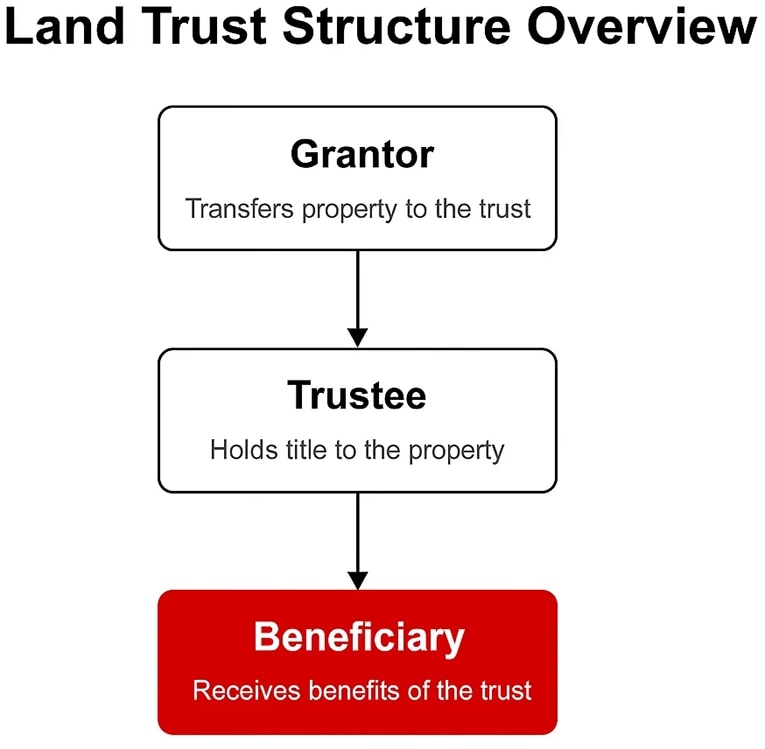
Roles of the Grantor, Trustee, and Beneficiary
A land trust typically involves three key parties: the grantor, the trustee, and the beneficiary.
- The grantor is the person or entity that creates the land trust and transfers ownership of the property to the trustee.
- The trustee is the person or entity that holds the title to the property and manages it according to the terms of the trust.
- The beneficiary is the person or entity that benefits from the trust, such as a family member or a charitable organization.
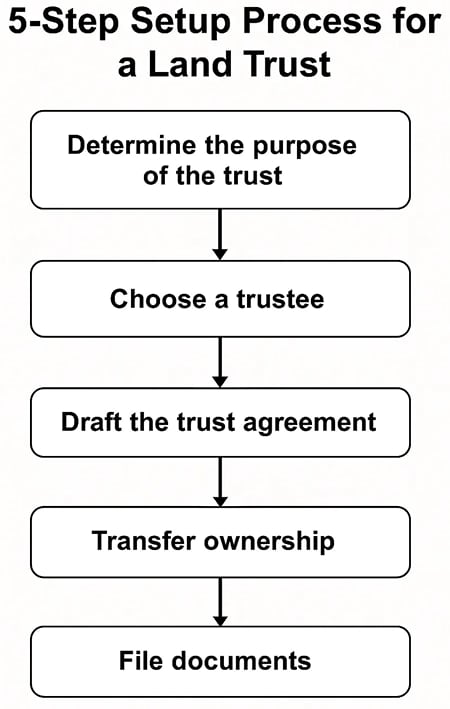
Process of Setting Up a Land Trust
Setting up a land trust typically involves the following steps:
- Determine the purpose of the trust: Identify the reason for creating the land trust, such as estate planning, asset protection, or conservation.
- Choose a trustee: Select a trustworthy individual or entity to serve as the trustee.
- Draft the trust agreement: Create a written agreement that outlines the terms of the trust, including the roles and responsibilities of the grantor, trustee, and beneficiary.
- Transfer ownership: Transfer ownership of the property to the trustee.
- File documents: File the trust agreement and other necessary documents with the relevant government agencies.
Benefits of Using a Land Trust
Using a land trust can provide several benefits, including:
- Privacy and Anonymity: Land trusts can maintain privacy and anonymity for property owners, as the title is held by the trustee, not the owner.
- Avoiding Probate: Land trusts can help avoid probate by enabling direct transfer of property after the owner's death, simplifying the process.
- Enhanced Liability Protection: Land trusts provide enhanced liability protection, reducing the property owner's risk of lawsuits or other legal issues.
- Separation of Assets: Land trusts can help property owners keep real estate investments separate and organized from other assets.
- Asset protection: Land Trusts can shield assets from creditors, providing an additional layer of protection for the owner.
- Tax benefits: Using land trusts might lead to tax benefits like reduced property taxes or increased deductions.
- Flexibility: Land trusts cater to a diverse range of intentions including conservation, development, or rental income generation.
Compared to other ownership structures, such as tenancy in common, a land trust offers an extra layer of privacy by keeping ownership details confidential through the trustee.
Privacy and Anonymity
One of the primary benefits of a land trust is the ability to maintain privacy and anonymity. When a property is held in a land trust, the trustee holds the title to the property, rather than the individual or entity that created the trust. This can provide a level of anonymity for the property owner, as the public records will show the trustee's name rather than the property owner's name.
Avoiding Probate
Another benefit of a land trust is the ability to avoid probate. When a property is held in a land trust, the trustee is responsible for managing the property, rather than the property owner's estate. This can simplify the process of transferring ownership of the property after the property owner's death, as the trustee can manage the property and ensure that it is transferred to the intended beneficiary.
Enhanced Liability Protection
Land trusts can also provide enhanced liability protection for property owners. When a property is held in a land trust, the trustee is responsible for managing the property, which can reduce the liability of the property owner. This can be particularly beneficial for property owners who are concerned about potential lawsuits or other legal issues.
Keeping Real Estate Investment Property Separate from Other Assets
Finally, land trusts can be used to keep real estate investment property separate from other assets. This can be particularly beneficial for property owners who have multiple properties or investments, as it can help to keep their assets separate and organized.
Setting Up a Land Trust
Identifying Trustees
When setting up a land trust, it's essential to identify the right trustee. The trustee is responsible for managing the property and making decisions on behalf of the trust. It's crucial to choose a trustworthy and reliable individual or entity to serve as the trustee.
Determining Which Assets to Hold in the Trust
Next, you need to determine which assets to hold in the trust. This can include real estate, cash, stocks, bonds, or other types of assets.
Choosing a Beneficiary
The beneficiary is the person or entity that will benefit from the trust. This can be a family member, a charity, or another entity. When choosing a beneficiary, it's essential to consider their needs and goals, as well as your own. You should also ensure that the beneficiary is aware of their role and responsibilities in the trust.
Creating the Trust Document
The trust document is the legal agreement that outlines the terms of the trust. It should include the following:
- The purpose of the trust
- The assets to be held in the trust
- The trustee's responsibilities
- The beneficiary's rights and responsibilities
- Any other relevant terms and conditions
It's essential to have a qualified attorney draft the trust document to ensure that it is legally binding and enforceable.
Turning Knowledge into Action
If you're ready to put your new knowledge on land trusts to good use, why not start looking at properties to invest in right away? We have an extensive list of commercial real estate properties for sale.
